
By extension, these elements also have high boiling points. The exception is mercury, which is a liquid at room temperature. The transition metals, as a group, have high melting points.Most transition metals are grayish or white (like iron or silver), but gold and copper have colors not seen in any other element on the periodic table. Transition metals look shiny and metallic.The transition metals are malleable (easily hammered into shape or bent).They are excellent conductors of heat and electricity.Therefore, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius.
#CHEMICAL ELEMENT SN FREE#
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus.
#CHEMICAL ELEMENT SN SERIES#
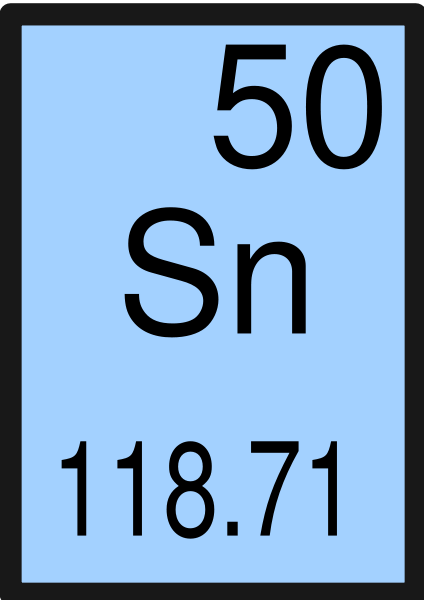
The electro positivity of the elements also reduces while moving down the reactivity series of metals. The reducing ability of the metals grows weaker while traversing down the series. These metals tarnish/corrode very easily. It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The metals at the top of the reactivity series are powerful reducing agents since they are easily oxidized. The atomic radius of Tin atom is 139pm (covalent radius). Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. Fast Facts: Tin Element Name: Tin Element Symbol: Sn Atomic Number: 50 Atomic Weight: 118. Here is a collection of tin element facts. It is known for its use for early canned goods and in the manufacture of bronze and pewter. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. Tin is silver or gray metal with atomic number 50 and element symbol Sn.

Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Tin are 112-124. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-911960896-5bbba09cc9e77c005857689e.jpg)
The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.įor stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. Tin is a chemical element with atomic number 50 which means there are 50 protons in its nucleus. Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in Tin


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
